Reducing Carbon at the Cement Plant
Since the launch of the Roadmap, substantial progress has been made. We are very proud of what the industry has accomplished together so far and are excited to see what’s next.
 In the Roadmap, ACA recommended a swift and widespread shift from regular cement to portland-limestone cement (PLC), a mix that is already widely used in Europe and can immediately reduce CO2 emissions by about 10%.
In the Roadmap, ACA recommended a swift and widespread shift from regular cement to portland-limestone cement (PLC), a mix that is already widely used in Europe and can immediately reduce CO2 emissions by about 10%.
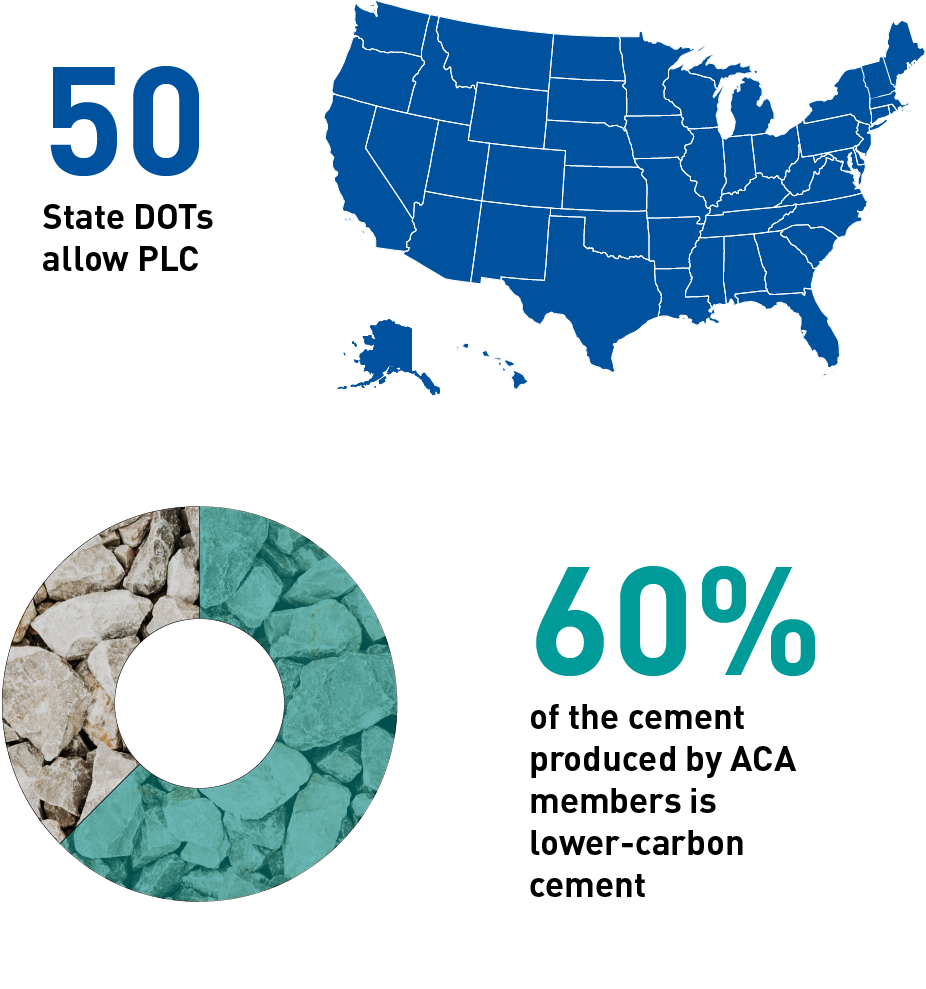
As of 2024, excitingly, all 50 state Departments of Transportation, major consumers of cement, have formally approved the use of PLC.
In California alone, the shift to PLC could result in 786,000 tonnes of CO2 potentially saved per year if a 100% shift to PLC occurred.
As of October 2024, approximately 60% of the cement produced by ACA members is lower-carbon cement, with some companies exclusively producing PLC.
The cement industry has also called for increased funding for research and development for carbon capture, utilization and storage – CCUS. The recently passed Inflation Reduction Act has provided important updates, including greater incentives for the cement industry to develop, install and operate carbon capture and storage technologies at its facilities.
We are taking a lead in pilot projects, testing the commercial use of carbon capture in partnership with the Department of Energy, with six projects currently underway at U.S. cement plants.
Cement manufacturers are constantly pushing efficiency and looking for available, lower-carbon fuel for plants. The industry has reduced traditional fossil fuels by 16%, with 60 plants using lower-carbon sources of energy.
